1. Runner’s knee.
This is a common overuse injury. Runner’s knee has several different causes. It often happens when your kneecap is out of alignment.
Over time, the cartilage on your kneecap can wear down. When that happens, you may feel pain around the kneecap, particularly when:
- Going up or down stairs
- Squatting
- Sitting with the knee bent for a long time
2. Stress fracture.
This is a small crack in a bone that causes pain and discomfort. It typically affects runners in the shin and feet. It’s often due to working too hard before your body gets used to a new activity.
Pain gets worse with activity and improves with rest. Rest is important, as continued stress on the bone can lead to more serious injury.
3. Shin splint.
This is pain that happens in the front or inside of the lower leg along the shin bone (tibia). Shin splints are common after changing your workout, such as running longer distances or increasing the number of days you run, too quickly. Pain wise, they can be hard to distinguish from a stress fracture of the shin, but the pain is usually more spread out along the bone. Also, an xray is normal.
People with flat feet are more likely to develop shin splints.
Treatment includes:
- Rest
- Stretching exercises
- Slow return to activity after several weeks of healing
4. Achilles tendinopathy.
Formerly called tendinitus, this is inflammationof the Achilles tendon. That’s the large tendon that attaches the calf to the back of the heel.
Achilles tendinitis causes pain and stiffness in the area of the tendon, especially in the morning and with activity. It is usually caused by repetitive stress to the tendon. Adding too much distance to your running routine can cause it. Tight calf muscles can also contribute.
Treatment includes:
- Rest
- Icing the area
- Calf stretches
5. Muscle pull.
This is a small tear in your muscle, also called a muscle strain. It’s often caused by overstretching a muscle. If you pull a muscle, you may feel a popping sensation when the muscle tears.
- Hamstrings
- Quadriceps
- Calf
- Groin
6. Ankle sprain.
This is the accidental stretching or tearing of ligaments surrounding the ankle. It often happens when the foot twists or rolls inward.
Sprains typically get better with rest, ice, compression, and elevating the foot.
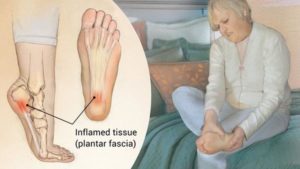 7. Plantar fasciitis
7. Plantar fasciitis
. An inflammation of the plantar fascia. That’s the thick band of tissue in the bottom of the foot that extends from the heel to the toes.
People with tight calf muscles and a high arch are more prone to plantar fasciitis. Although it may be linked to adding activity, plantar fasciitis can also happen without any obvious reason.
Treatment includes:
- Calf stretches
- Rest
- Icing the bottom of the foot
- Wearing good shoes at all times (even at home or on the beach)
8. IT (iliotibial) band syndrome.
This syndrome causes pain on the outside of the knee. The IT band is a ligament that runs along the outside of the thigh, from the top of the hip to the outside of the knee.
IT band syndrome happens when this ligament thickens and rubs the knee bone, causing inflammation.
Treatment includes:
- Cutting back on exercise
- Heat and stretching before exercise
- Icing the area after activity
9. Blisters.
These are fluid-filled sacks on the surface of the skin. They are caused by friction between your shoes/socks and skin.
To help prevent blisters:
- Start using new shoes gradually
- Wear socks with a double layer
- Apply petroleum jelly on areas prone to blisters
10. Temperature-related injuries.
These include:
- Sunburn
- Heat exhaustion
- Frostbite
- Hypothermia
You can prevent these by dressing appropriately, staying hydrated, and using sunscreen
